Research
Summary of the various research activities carried out in the ABS group.
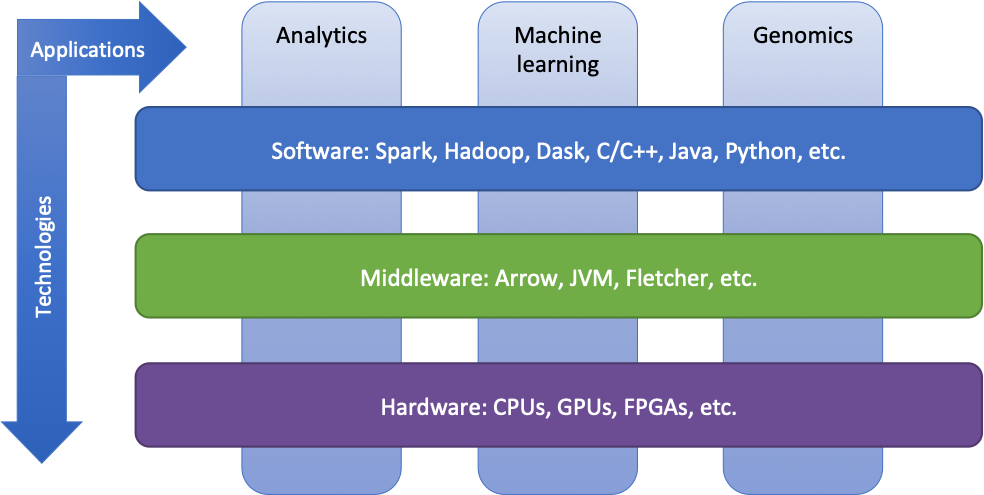
Technologies
Research in the ABS group focuses on a number of horizontal technology layers in the big data stack. At the top layer, we perform optimizations to increase the efficiency of software developed using big data frameworks such as Apache Spark. In the middleware layer, we develop efficient interfaces such as Apache Arrow to allow software components (such as JVM) to communicate efficiently with the hardware. And at the hardware layer, we develop optimized CPU or GPU implementations in addition to customized FPGA IP.
Application domains
We use these technologies to target multiple application domains, focussed on genomics, machine learning and data analytics. The field of genomics and personalized medicine is becoming extremely data-driven. This is due to the dramatic decrease in the price of DNA sequencing in the past decade, which resulted in shifting the bottleneck in DNA analysis from acquiring the DNA data to the actual processing and analysis of this data. Our group is working to streamline the whole genomic computational pipeline starting from data storage and transfer, all the way to data analysis and interpretation. Important collaborators in this field are Utrecht University Medical Center, Erasmus Medical Center and our own startup Bluebee.
Another application domain the group focuses on is machine learning, which is becoming a central theme in the analysis of big data volumes. Collaborations between our group and a number of industrial partners have shown the viability of machine learning algorithms in various applications ranging from predictive maintenance to fraud detection. In addition, Spark is being used to enable the reliable in-memory computation of big data volumes, thereby reducing the bottleneck incurred by hard disk access for memory intensive tasks. A whole host of big data analytics algorithms are being developed to manage the continuously increasing volumes of data. Important collaborators in this field are IBM, Philips Healthcare and Leiden University Medical Center.
Current projects
Fitoptivis: From the cloud to the edge – smart IntegraTion and OPtimisation Technologies for highly efficient Image and VIdeo processing Systems
Fitoptivis is a European project with 31 partners across 5 countries targeting high-performance distributed image processing systems. The project balances power demand versus performance of the increasingly complex distributed configurations in Cyber-Physical Systems, reflected in the growing number of sensors, actuators and other smart devices, their growing autonomy, and the increased need for performance. This complexity increases even more when multiple heterogeneous sensor inputs are combined for analysis and through integration of both generic and specialized devices. On top of that, CPS need to satisfy rigorous constraints on real-time behavior, safety, security, reliability, quality, performance and energy consumption. Fitoptivis provides end-to-end multi-objective optimization for imaging and video pipelines of CPS, with an emphasis on the latter two elements: energy and performance.
NewControl: New Integrated Control System for Next Generation Autonomous Vehicles
NewControl is a European project with 27 partners across 8 countries targeting next generation control systems for autonomous vehicles. The project develops virtualized platforms for each vehicular sub-system essential to autonomous operation at SAE Level 3+. Each of these unifies the critical components required to realize a specific function: perception, cognition, control – through vertical integration within an adaptive (not rigid) architectural framework. The resulting virtual platforms effectively deliver specific functionalities as services to the vehicular platform, abstracting internal implementation, enabling portability to different application domains, and facilitating modular development of automation that is guaranteed as safe by design.
Completed projects
Almarvi: Algorithms, Design Methods, and Many-core Execution Platform for Low-Power Massive Data-Rate Video and Image Processing
Almarvi is a European project with 13 partners across 4 countries targeting many-core execution platforms for image processing applications. The project focuses on reducing overall system design cost and time-to-market and enabling low cost solutions for high volume markets in different industrial domains and creating new market opportunities, and supporting SMEs. The demonstrators developed in this project for the healthcare, security/surveillance/monitoring, and mobile use cases are designed to directly lead to marketable applications and products in their relevant domains. Integrated releases of Almarvi image/video processing algorithm libraries, reference design tools and platforms, and system software stack solutions are made available along with their evaluation for the demonstrated use cases.
Benefic: Best ENergy EFficiency solutions for heterogeneous multI-core Communicating systems
Benefic is a European project with 20 partners across 3 countries taking a holistic approach in integrating new sources of energy harvesting, distributing energy closer to where it is used. New methods developed in this project aim to improve power efficiency at the architecture-definition level, prediction and management strategies on power consumption. The trend is towards heterogeneous platforms, which includes sophisticated on-chip communication infrastructures for higher energy efficiency and performances. Moreover, heterogeneous many-cores provide a sound balance between performance and power consumption. The project targets high energy-efficient design solutions, responding to the complexity increase in mobile equipment.
Comcas: Communication-centric heterogeneous multi-core architectures
Comcas is a European project with 13 partners across 2 countries targeting power efficiency for mobile multi-core platforms. Mobile communications are the most important consumer electronics market worldwide. Yet as features and customer expectations grow, they run up against the same brick wall of battery life. Only by reducing power consumption can manufacturers introduce innovative new features. The challenge for Comcas is to improve battery life significantly for small-form-factor devices by reducing power consumption.
Smecy: Smart Multi-core Embedded SYstems
Smecy is a European project with 27 partners across 9 countries which aims to develop new programming technologies enabling the efficient exploitation of multi-core architectures. The vision of the SMECY consortium is that a holistic approach for the integration of multi-core SoC and embedded software technologies is required. To find such an approach, interactive research and development of programming and design methods, multi-core architectural solutions and associated supporting tools are needed. All of this is strongly driven by the requirements and constraints from different application areas as
well as the target.
